3 Types of Sequence Prediction Problems
Understanding your problems before implementing your sequence prediction model.
]](/assets/img/posts/three-types-sequence-prediction-problems-01.jpg)
Sequence prediction is a popular machine learning task, which consists of predicting the next symbol(s) based on the previously observed sequence of symbols. These symbols could be a number, an alphabet, a word, an event, or an object like a webpage or product. For example:
- A sequence of words or characters in a text
- A sequence of products bought by a customer
- A sequence of events observed on logs
Sequence prediction is different from other types of supervised learning problems, as it imposes that the order in the data must be preserved when training models and making predictions.
Sequence prediction is a common problem which finds real-life applications in various industries. In this article, I will introduce to you three types of sequence prediction problems:
- Predicting the next value
- Predicting a class label
- Predicting a sequence
Predicting the next value
Being able to guess the next element of a sequence is an important question in many applications. A sequence prediction model learns to identify the pattern in the sequential input data and predict the next value.

Time-series forecasting
Time-series refers to an ordered series of data, where the sequence of observations is sequentially in the time dimension. Time-series forecasting is about making predictions of what comes next in the series. Thus, Time-series forecasting involves training the model on historical data and using them to predict future observations.
But what makes time-series forecasting different from a regression problem? There are 2 things:
- Time series is time-dependent, which is ordered by time. But Regression can be applied to non-ordered data where a target variable is dependent on values taken by features.
- Time series looks for seasonality trends. For example, the power demand in a day will drop at night, and the number of air passengers will increase during the summer.
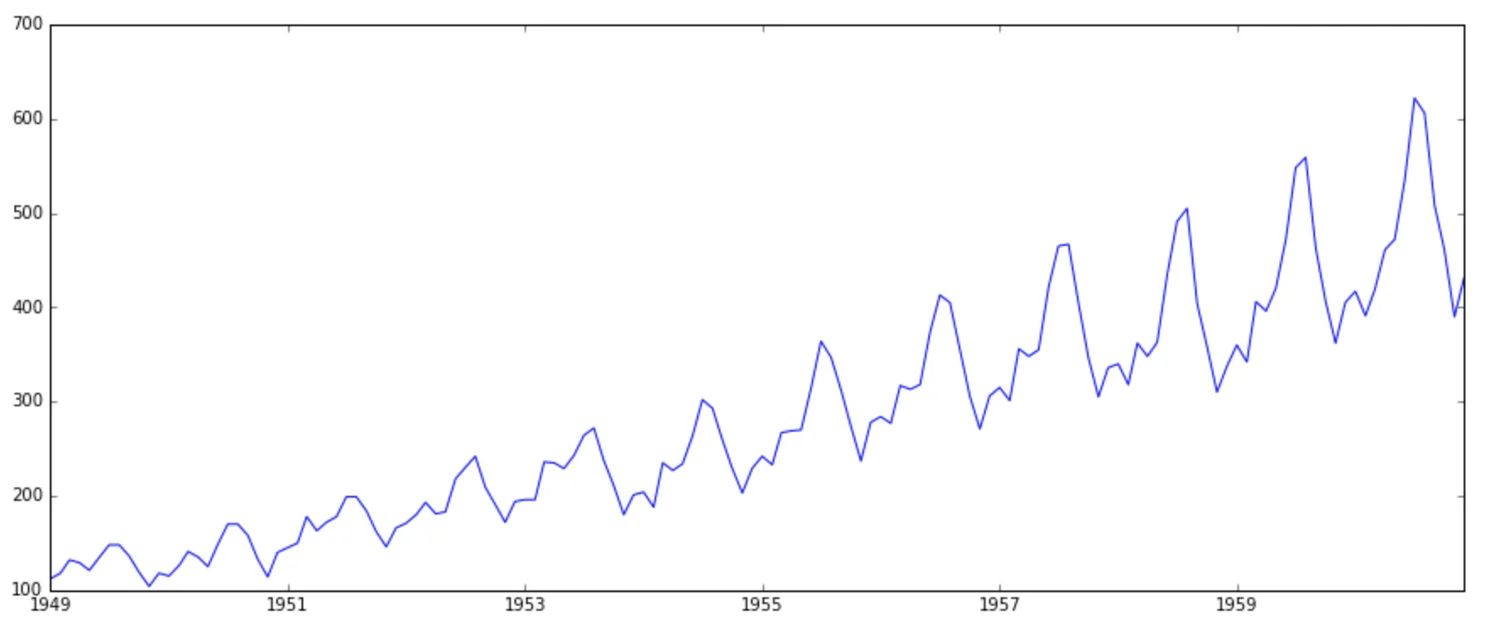
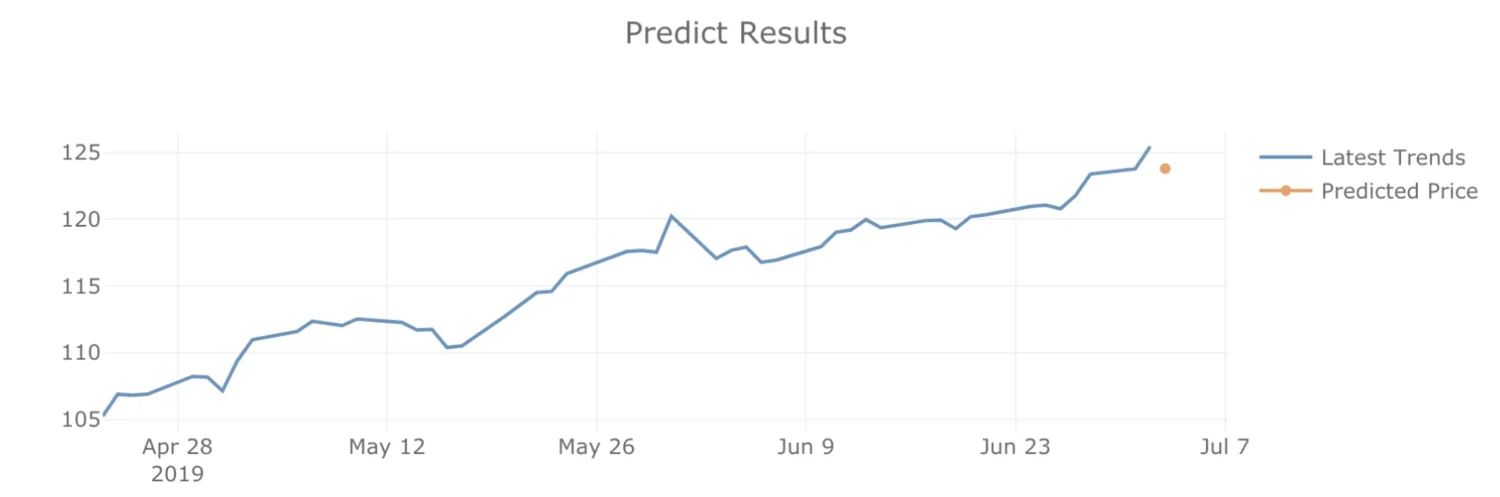
You can try to build your time-series forecasting model with LSTM or ARIMA on the Air Passengers dataset or try out this TensorFlow.js demo.
Webpage/product recommendation
Have you searched for something, and every advertisement you saw next is related to what you searched for?
For example, after watching the movie Avengers: Endgame, I was searching for explanations of certain scenes. Ever since then, Google Discover Feed started to show me content revolve around the Marvel Cinematic Universe, even until today.
Even though it seems like Google Discover Feed is recommending a collection of webpages, each webpage is an individual output.
Likewise, we can apply this idea to product recommendations. If we train a sequential prediction model with all the past transactions, we may be able to predict the next purchase for a customer.
Predicting a class label
Sequence classification uses labeled datasets with some sequence inputs and class labels as outputs, to train a classification model which can be used to predict the class label of an unseen sequence.

Some examples of sequence classification applications:
Text categorization. Assigning labels to documents written in a natural language has numerous real-world applications including sentiment classification and topic categorization.
Anomaly detection. Researchers explore detecting abnormal behaviors in 4 different time-series datasets, 1) electrocardiograms, 2) Space Shuttle Marotta valve, 3) power demand, and engine sensors datasets.
Genomic research. Researchers have been classifying protein sequences into categories. This work could be potentially useful for the discovery of a wide range of protein functions.
Health-informatics. Researchers use LSTM to classify electrocardiogram (ECG) signals into five different classes to identify the condition of a patient’s heart. This allows end-to-end learning, extracting features related to ECG signals without any expert intervention.
Brain-computer interface. We extract brain signals from the Electroencephalogram, decoding of the user’s intentions to operate the assistive devices.
Predicting a sequence
Sequence-to-sequence learning (Seq2Seq) is about training models to convert an input sequence and output another sequence. Like all supervised learning, Seq2Seq models are trained with a dataset of pairs, but the input sequences and output sequences can have different lengths.

This model consists of two LSTMs; one will serve as an encoder, which encodes the input sequence and producing internal state representation. These representations encode the “meaning” of the input sequence and are serve as input for the decoder, which is responsible for generating the target sequence. In practice, training for a Seq2Seq model is done by “forcing” the decoder to generate perfect sequences and penalizing it for generating a wrong sequence.
Machine translation
“There is a white cat,” translates to “Il y a un chat blanc.” A Seq2Seq model frees us from sequence length and order, which makes it ideal for the translation of languages. Before Neural Machine Translation, machine translation was rule-based, focusing on word-by-word relationships and using Context Free Grammar.
In 2013, Sutskever et al. introduced a Seq2Seq architecture for machine translation, while Cho et al. proposed an Encoder and Decoder architecture. Over the past few years, the development in this area is very active. The current state-of-the-art machine translation implemented for Google Translate is Attention and Transformer based.
Image caption generation
Automatically generating natural language descriptions according to the content observed in an image has attracted many researchers in the field of artificial intelligence. This is challenging because it combines the knowledge of computer vision and natural language processing, involving object detection to infer objects and objects’ relationships in an image and learning the grammar to generate text descriptions.
Vinyals et al. introduced an end-to-end neural network consisting of a vision convolutional neural network followed by a language generating recurrent neural network.

In this model, the encoder is a convolutional neural network that extracts features in the image. The decoder is a recurrent neural network, mainly used for generating text descriptions. Similar to machine translation, the current state-of-the-art uses attention mechanism, where the network pays attention to parts of the input and the allocation of limited information processing resources to those important parts.